Ketofol, Etomidate and Thiopental/Propofol Compared: Retrospective Study From Turkey
Out on PubMed, from investigators in Turkey and the Netherlands, is this study:
The superiority of ketofol and etomidate against propofol or thiopental anesthesia for ECT.
Asian J Psychiatr. 2022 Apr 1;72:103090. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2022.103090. Online ahead of print. PMID: 35390580

The abstract is copied below:Objectives: Most anesthetic drugs used for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) have dose-dependent anticonvulsive effects, counter-acting seizure induction, lowering seizure quality. However, a consummate drug for ECT anesthesia has not yet been established. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of etomidate, thiopental, propofol and co-administration of ketamine-propofol (ketofol) on seizure quality and hemodynamic safety.Methods: Registries of 121 patients (1077 sessions) were retrospectively evaluated. The effects of anesthetics on ECT-related parameters (stimulation charge, central seizure duration, number of failed stimulation trials, mean arterial pressure, and peak heart rate) were analyzed via linear mixed-effects models.Results: Overall, the seizure duration decreased, and the stimulation charge increased in time with continuing sessions within a course of ECT. The decrease in seizure duration and the increase in required stimulation charge was significantly lower with etomidate and ketofol. Additionally, ketofol was significantly related to a lower number of failed stimulation trials compared to propofol. Ketofol and propofol use was associated with a significantly lower postictal mean arterial pressure.Conclusion: Ketofol and etomidate were equivalently superior in the rate of decrease in seizure duration and the required elevation in stimulus charge, which would interpret into valuable clinical guidance, especially for "seizure resistant" patients, and their use may potentially lower ECT related cognitive side effects.Keywords: Electroconvulsive Therapy; Etomidate; Ketamine; Propofol; Thiopental.The article is here.And from the text:
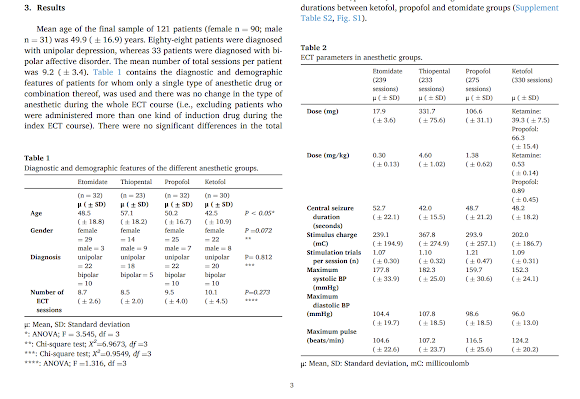
 Here is yet another study comparing comparing seizure parameters and hemodynamics between induction agents. It has a very pro-etomidate and ketofol bent.
Here is yet another study comparing comparing seizure parameters and hemodynamics between induction agents. It has a very pro-etomidate and ketofol bent.

The abstract is copied below:Objectives: Most anesthetic drugs used for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) have dose-dependent anticonvulsive effects, counter-acting seizure induction, lowering seizure quality. However, a consummate drug for ECT anesthesia has not yet been established. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of etomidate, thiopental, propofol and co-administration of ketamine-propofol (ketofol) on seizure quality and hemodynamic safety.Methods: Registries of 121 patients (1077 sessions) were retrospectively evaluated. The effects of anesthetics on ECT-related parameters (stimulation charge, central seizure duration, number of failed stimulation trials, mean arterial pressure, and peak heart rate) were analyzed via linear mixed-effects models.Results: Overall, the seizure duration decreased, and the stimulation charge increased in time with continuing sessions within a course of ECT. The decrease in seizure duration and the increase in required stimulation charge was significantly lower with etomidate and ketofol. Additionally, ketofol was significantly related to a lower number of failed stimulation trials compared to propofol. Ketofol and propofol use was associated with a significantly lower postictal mean arterial pressure.Conclusion: Ketofol and etomidate were equivalently superior in the rate of decrease in seizure duration and the required elevation in stimulus charge, which would interpret into valuable clinical guidance, especially for "seizure resistant" patients, and their use may potentially lower ECT related cognitive side effects.Keywords: Electroconvulsive Therapy; Etomidate; Ketamine; Propofol; Thiopental.The article is here.And from the text:



Please see also blog post of April 10, 2022 for a similar study. This is a retrospective chart review; and without antidepressant efficacy and cognitive data, the implications of the findings are somewhat limited. Again, one of the main questions raised by this type of research is how much ketofol will catch in in popularity as an induction agent for ECT.
Followers of the ECT anesthesia literature will want to read this paper in full, ~15 minutes.



Comments
Post a Comment