Gene Expression of Kynurenine Pathway Enzymes in Depression and Following ECT: New Data From Ireland
Out on PubMed, from researchers in Ireland, is this study:
Gene expression of kynurenine pathway enzymes in depression and following electroconvulsive therapy.Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2024 Oct 17:1-10. doi: 10.1017/neu.2024.34. Online ahead of print.
PMID: 39417574

The abstract is copied below:
Objective: This study aimed to investigate changes in mRNA expression of the kynurenine pathway (KP) enzymes tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenase (TDO), indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 and 2 (IDO1, IDO2), kynurenine aminotransferase 1 and 2 (KAT1, KAT2), kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO) and kynureninase (KYNU) in medicated patients with depression (n = 74) compared to age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 55) and in patients with depression after electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Associations with mood score (24-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, HAM-D24), plasma KP metabolites and selected glucocorticoid and inflammatory immune markers known to regulate KP enzyme expression were also explored.
Methods: HAM-D24 was used to evaluate depression severity. Whole blood mRNA expression was assessed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
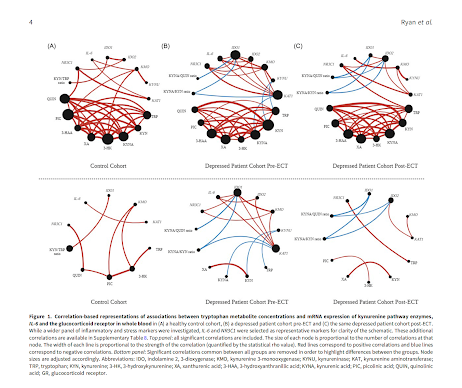
Results: KAT1, KYNU and IDO2 were significantly reduced in patient samples compared to control samples, though results did not survive statistical adjustment for covariates or multiple comparisons. ECT did not alter KP enzyme mRNA expression. Changes in IDO1 and KMO and change in HAM-D24 score post-ECT were negatively correlated in subgroups of patients with unipolar depression (IDO1 only), psychotic depression and ECT responders and remitters. Further exploratory correlative analyses revealed altered association patterns between KP enzyme expression, KP metabolites, NR3C1 and IL-6 in depressed patients pre- and post-ECT.
Conclusion: Further studies are warranted to determine if KP measures have sufficient sensitivity, specificity and predictive value to be integrated into stress and immune associated biomarker panels to aid patient stratification at diagnosis and in predicting treatment response to antidepressant therapy.
Keywords: Depression; electroconvulsive therapy; glucocorticoid receptor; interleukin-6;
The article is here.
And from the text:
This is a dense biochemistry lesson about the kynurenine pathway (KP) from an obviously expert research team. While the results are largely negative and the limitations many, there are certainly important signals about altered gene expression of KP enzymes in depression, and subsequent treatment with ECT. Kudos to this team; we look forward to their future work in this area.






Comments
Post a Comment